Demystifying Your Legal Rights to Emotional Support Animals
Every year, more and more adults turn to Emotional Support Animals for relief from conditions like anxiety and depression. Nearly one in five Americans experience mental health challenges, making the search for compassionate support crucial. Understanding how these unique companions differ from service animals and what protections actually exist can help American pet owners find real comfort and avoid legal confusion.
What Are Emotional Support Animals
Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) provide therapeutic companionship for individuals experiencing mental health challenges. Unlike service animals, these companion pets offer emotional comfort without requiring specialized training in specific tasks.
According to the American Kennel Club, ESAs are pets prescribed by licensed mental health professionals to individuals with diagnosed mental health conditions. These animals help alleviate symptoms through their presence and emotional connection, offering significant psychological benefits.
The key characteristics of Emotional Support Animals include:
- Prescribed by licensed mental health professionals
- Provide comfort for mental health conditions
- Not required to have specialized service animal training
- Can include various animal species
- Primarily focused on emotional and psychological support
Unlike service animals, emotional support animals are not recognized under the Americans with Disabilities Act and do not have the same legal protections or public access rights. Their primary purpose is to offer companionship and emotional stability for individuals managing mental health challenges.
Pro Tip – ESA Documentation: Always obtain an official letter from a licensed mental health professional that specifically describes your need for an Emotional Support Animal to ensure proper recognition and potential housing accommodations.
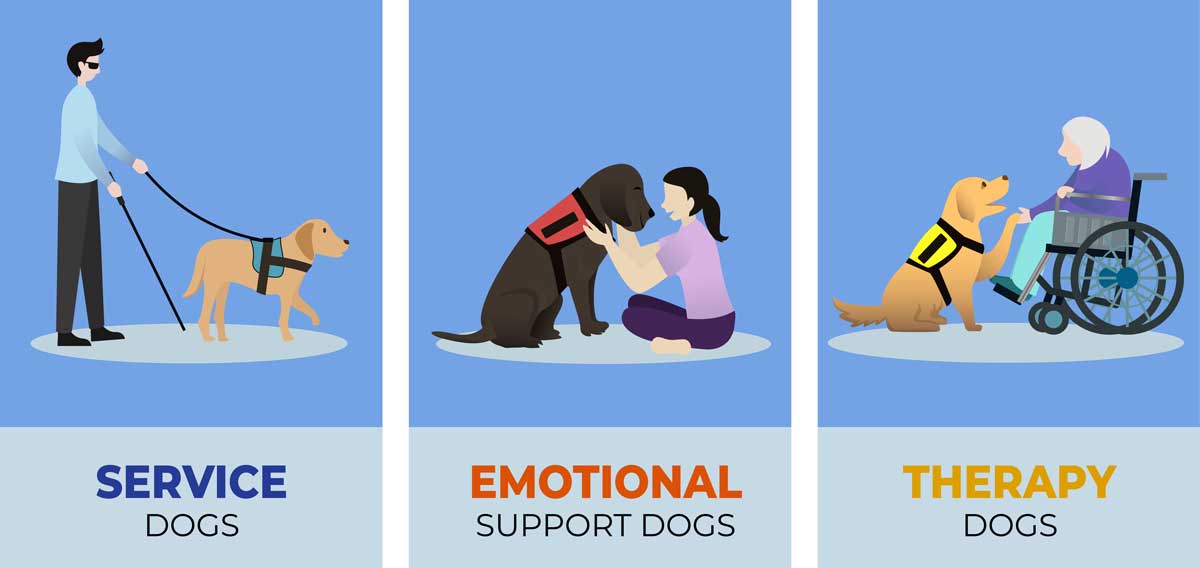
Types of Support Animals and Key Differences
Support animals play critical roles in assisting individuals with various health challenges, but they are not all created equal. Understanding the distinctions between different types of support animals is crucial for recognizing their unique purposes and legal protections.
Service animals represent the most specialized category, trained to perform specific tasks for individuals with disabilities. These animals, typically dogs, are highly skilled and have extensive legal protections under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Their training enables them to assist with physical tasks like guiding visually impaired individuals, alerting deaf persons to sounds, or helping individuals with mobility challenges.
Key differences between support animal types include:
- Service Animals:
- Specifically trained to perform tasks
- Legally protected under ADA
- Allowed in all public spaces
- Typically dogs or miniature horses
- Must perform specific disability-related functions
- Emotional Support Animals:
- Provide psychological comfort
- No specialized task training required
- Limited legal protections
- Can be various animal species
- Require mental health professional documentation
- Therapy Animals:
- Provide comfort in therapeutic settings
- Work in hospitals, schools, nursing homes
- Require temperament and behavior certification
- Not granted same legal access as service animals
According to the American Kennel Club, the key distinction lies in the animal’s specific purpose and level of training. Service animals have precise, task-oriented roles, while emotional support animals offer companionship and psychological relief.

Here’s a concise comparison of the main types of support animals and their core distinctions:
| Animal Type | Required Training | Legal Protections | Typical Roles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service Animal | Extensive, task-based | Full ADA and public access rights | Physical disability support |
| Emotional Support | None required | Housing (Fair Housing Act) only | Mental health companionship |
| Therapy Animal | Behavior certification | No public or housing access rights | Visits hospitals, group care |
Pro Tip – Support Animal Verification: Always obtain official documentation from a licensed professional to clearly define your support animal’s specific category and understand its corresponding legal rights and limitations.
How to Qualify for an Emotional Support Animal
Emotional Support Animal (ESA) qualification involves a specific legal and medical process that requires careful documentation and professional evaluation. Understanding the steps can help individuals navigate this important healthcare support mechanism effectively.

Obtaining an official ESA recommendation begins with a comprehensive mental health assessment. This process requires working closely with a licensed mental health professional who can diagnose a qualifying mental health condition and determine whether an emotional support animal would provide therapeutic benefits.
The qualification process typically involves several key steps:
- Mental Health Evaluation:
- Schedule a comprehensive psychological assessment
- Discuss current mental health challenges
- Determine potential benefits of an emotional support animal
- Verify eligibility for ESA prescription
- Professional Documentation:
- Request an official ESA letter from your mental health provider
- Ensure letter includes specific diagnosis
- Confirm professional recommendation for animal support
- Validate need for emotional and psychological assistance
- Animal Selection:
- Choose an animal compatible with your lifestyle
- Consider temperament and living situation
- Evaluate potential animal’s ability to provide comfort
- Ensure animal meets basic behavioral standards
Pettable’s guidance emphasizes that the ESA letter is crucial, serving as official documentation that validates the animal’s therapeutic role. This letter must come from a licensed therapist, psychologist, or psychiatrist who has personally evaluated your mental health condition.
Pro Tip – Professional Consultation: Always work directly with a licensed mental health professional who understands the specific requirements for emotional support animal documentation and can provide a comprehensive, legally recognized evaluation.
Legal Protections Under Federal and State Law
Emotional Support Animals occupy a unique legal landscape with specific protections and limitations under federal and state regulations. Understanding these nuanced legal frameworks is crucial for individuals relying on these important companion animals.
Federal housing regulations provide critical protections for emotional support animal owners, particularly through the Fair Housing Act. This legislation ensures that individuals with documented mental health needs can live with their support animals, even in housing complexes with strict no-pet policies. The law requires landlords and property managers to make reasonable accommodations, preventing discrimination against tenants with emotional support animals.
Key legal protections for Emotional Support Animals include:
- Fair Housing Protections:
- Exemption from no-pet housing restrictions
- Protection against housing discrimination
- Reasonable accommodation requirements
- No additional pet fees or deposits
- Limited Public Access Rights:
- No guaranteed access to public spaces
- Unlike service animals, not protected under ADA
- Restricted entry to restaurants, stores, workplaces
- Dependent on individual establishment policies
- State-Level Variations:
- Additional protections in some states
- Potential workplace accommodation differences
- Varying interpretations of housing laws
- Supplemental legal frameworks beyond federal guidelines
According to the American Kennel Club, while emotional support animals have significant housing protections, they do not enjoy the same comprehensive public access rights as service animals. This means owners must carefully navigate different environments and understand the specific legal limitations.
Pro Tip – Legal Documentation: Always maintain current, professionally signed documentation for your emotional support animal, including a recent letter from a licensed mental health professional to substantiate your need for the animal in various legal contexts.

Risks, Limitations, and Common Pitfalls
Emotional Support Animals present unique challenges that extend beyond their therapeutic benefits. Individuals considering or currently utilizing these companion animals must navigate a complex landscape of legal, social, and practical considerations.
Airline policies have become increasingly restrictive regarding emotional support animals, highlighting the growing scrutiny these animals face in public spaces. Many transportation providers now limit ESA access, requiring extensive documentation and imposing strict behavioral standards that can create significant obstacles for owners.
Common risks and limitations include:
- Legal Complications:
- Potential fines for misrepresentation
- Limited public space access
- Complex housing negotiation requirements
- Risk of legal challenges without proper documentation
- Social Challenges:
- Public misunderstanding about ESA rights
- Potential stigma and negative perceptions
- Difficulty navigating social environments
- Increased scrutiny in professional settings
- Practical Constraints:
- Significant documentation requirements
- Ongoing professional mental health verification
- Potential additional costs for accommodations
- Complex travel and housing negotiations
According to the American Kennel Club, misrepresenting an animal as an emotional support animal can result in serious legal consequences. Many individuals inadvertently create problems by failing to understand the specific legal frameworks governing these animals.
This table summarizes potential challenges and how to proactively address them:
| Challenge Type | Example Issue | Proactive Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Legal | Risk of misrepresentation fines | Maintain up-to-date professional letters |
| Social | Misunderstandings in public spaces | Educate others on ESA limitations |
| Practical | Complicated airline policies | Research and comply with all requirements |
Pro Tip – Documentation Preparedness: Maintain a comprehensive, current ESA documentation folder with recent professional evaluations, clear animal identification, and behavioral certification to mitigate potential legal and social challenges.
Protect Your Rights with Expert Legal Support for Emotional Support Animals
Navigating the complex legal protections and limitations for Emotional Support Animals can feel overwhelming. Understanding your rights under housing laws, employment laws and dealing with documentation challenges are just some of the hurdles you might face. If you need help securing your legal rights or confronting unfair treatment related to your Emotional Support Animal, the experienced team at Goldberg & Loren is here to fight for you.
Don’t let confusion or legal obstacles stand in your way. Our firm’s extensive background in employment law and personal injury can provide you with the trusted guidance necessary to protect your interests. Contact Goldberg & Loren today for a free consultation over your situation and explore how we can assist with your legal needs connected to Emotional Support Animals and beyond. Act now to ensure your rights are fully respected and defended.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I sue my landlord or employer?
The biggest question we get at Goldberg & Loren, is if my employer or landlord does not accommodate my support dog, can I sue? The short answer is absolutely. Emotional support animals (ESAs) have protections primarily in housing under the federal Fair Housing Act (FHA) and under California’s Fair Employment and Housing Act (FEHA) in providing reasonable accommodations in disabilities. These are trained animals and thus, fall under protections.
What are the main differences between Emotional Support Animals and Service Animals?
Emotional Support Animals provide companionship and emotional support for individuals with mental health conditions, without specialized training for specific tasks, whereas Service Animals are specifically trained to assist individuals with disabilities by performing particular tasks.
What legal protections do Emotional Support Animals have?
Emotional Support Animals are protected under the Fair Housing Act, which allows them to live with their owners in housing that prohibits pets. However, they do not have the same public access rights as Service Animals under the Americans with Disabilities Act.
How can I qualify for an Emotional Support Animal?
To qualify for an Emotional Support Animal, you must undergo a mental health evaluation by a licensed professional, who will provide you with official documentation indicating your need for the animal based on your mental health condition.
What risks and limitations do Emotional Support Animal owners face?
Emotional Support Animal owners may face legal complications, social misunderstandings regarding their ESA rights, and practical constraints such as strict airline policies and the need for extensive documentation.

